With fiber deployments accelerating around the world and with operators seemingly on a daily basis announcing additional fiber expansion projects, there is no question that the competition for broadband subscribers and revenue is intensifying faster than some operators would prefer. Because of that intensification and because of the time and cost required for fiber network deployments, operators are increasingly using a range of technologies for their fiber networks. System vendors have made this easier by adopting combo optics and combo cards that can support a range of technologies, from 2.5G GPON to 25G PON, and potentially beyond. Equipment vendors have heard the call from their operator customers that they need to have every tool available to them to succeed in a highly-competitive environment.
Although operators are, for the most part, still in the early stages of deploying gigabit and multi-gigabit services using XGS-PON, their fiber expansions are opening up additional opportunities for applications and new addressable customers that already require speeds beyond what XGS-PON can provide. For example, large enterprises and campus environments, which have typically been served by point-to-point Ethernet connections, are increasingly being passed by PON ODNs, especially those enterprises that are adjacent to residential neighborhoods.
Though the ITU (International Telecommunication Union) has determined that single channel 50G PON as defined in its G.hsp.50pmd specification is the next generation technology it will move forward with, the increasing use cases for PON combined with those use cases requirements for additional speeds beyond what XGS-PON can provide have opened the door for 25G PON as an important tool in operators’ toolboxes. The current strength in fiber buildouts and the need to address new use cases today has resulted in a list of operators who simply can’t wait for 50G PON to be fully standardized, tested, and productized.
In today’s hypercompetitive broadband market, timing and the availability of the right technology tools are everything. Although 50G PON provides a tremendous theoretical boost in speeds, the timeline for its availability is still an open question. China Mobile is on the record saying that it will begin limited deployments of 50G PON beginning in 2023. However, the CAICT (China Academy of Information and Communications Technology) has stated that it believes mass-market deployments of 50G PON won’t occur until the second half of this decade. With XG-PON deployments just hitting their stride as of last year and a typical deployment cycle of around 5-7 years for each new technology, the CAICT’s estimate seems to be more realistic. Even if we split the difference, the market is still looking at 2025 as the earliest point at which 50G PON sees meaningful deployments for residential applications.
One of the biggest challenges to overcome for all 50G PON component suppliers and equipment vendors is the increased optical power budget required. Additionally, the proposed integration of DSPs (Digital Signal Processors) is a significant change, as they have not been required in PON technologies before. Incorporating DSPs theoretically allows for the use of lower-cost 25G optics, which are widely available and mature. DSPs allow for the support of both OOK (On-Off keying) and OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access). This support is critical for operators as it allows them to re-use their existing ODN (Optical Distribution Network) and not have to make significant and costly changes that could impact thousands of subscribers.
DSP-enhanced PON technologies are already being put through their paces, with China Mobile having demonstrated transmission rates of 41G downstream and 16G upstream in a hybrid environment using a 50G PON ONT as well as a 10G PON ONT. Meanwhile, Nokia has demonstrated 100G PON in conjunction with Vodafone at a lab in Germany. Both trials occurred in 2021 and more proof-of-concept work is expected throughout this year.
This brings us back to 25G PON. Although the traditional method of developing a technology for wide-scale deployment is to work through one of the primary standards bodies (ITU and IEEE), that avenue was closed to Nokia and other component suppliers and service providers who were interested in seeing both 25G PON and 50G PON standardized through the ITU, as well as accelerating the availability of 25G PON technologies to bridge the gap between today’s 10G technologies and tomorrow’s 50G and 100G options. So, the collection of vendors and operators organized the 25GS-PON MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) to develop standards, define interoperability, and generally help to evolve the technology outside the traditional standards organizations. The group’s members include AT&T, Chorus, Chunghwa Telecom, Cox Communications, NBN, Opticomm, and Proximus—service providers with the collective buying power to make the R&D effort worthwhile for the growing list of component and equipment vendors who are also members.
CableLabs, which focuses on developing standards and technologies on behalf of its cable operator members, is also a member of the MSA. Just like their telco counterparts, cable operators are trying to determine their bandwidth requirements in residential networks over the next few years, so having a choice among technology options is important. But unlike telcos, cable operators also have to determine whether they will satisfy these future bandwidth requirements with DOCSIS 4.0 and their existing coax plant or whether they will do so with fiber. In both cases, 25G PON is being examined as both a residential technology beyond current 10G DPoE (DOCSIS Provisioning over EPON) options and also as a potential aggregation technology for both remote PHY and remote MACPHY nodes.
CableLabs is also working on its own initiatives, including single wavelength 100G Coherent PON, which is seen as an ideal long-term option for cable operators who have wide ranges of fiber span lengths (up to 80km) and need spit ratio sizes that are more akin to today’s service group sizes of 200-500 homes passed per node. Nevertheless, the timeline for 100G Coherent PON, like 50G PON, is still being determined.
Expanding use cases for PON driving the need for 25G
Beyond the uncertain timing of 50G PON, as well as the desire for technology choice, one of the primary reasons for the short-term demand for 25G PON is simply the desire to use PON in applications that go well beyond traditional residential broadband access. It is actually in these applications where 25G PON will see the most deployments, particularly within the next 2-3 years.
Enterprise services have typically been point-to-point Ethernet connections. But as operators expand their PON ODNs to support residential and small-medium business applications, 25G PON can be implemented to deliver symmetric 10G connections, comparable or better than what enterprises are accustomed to. Because 25G PON has been designed to co-exist with both GPON and XGS-PON, service providers can have the flexibility of using the same OLT to deliver both high- and low-SLA traffic or they can split that traffic and customer base across multiple OLTs. Either way, the existing ODN remains intact.
Additionally, service providers are also interested in 25G PON their 5G transport networks, particularly in the case of small cell transport. Though LTE networks never resulted in the type of volume deployments of PON equipment to support backhaul, there is more consensus that the PON technology options available now provide the bandwidth (symmetric 10G) along with the latency requirements necessary to support 5G services and corresponding SLAs.
Clear Upgrade Path
Though standards bodies have traditionally defined which technologies get adopted and when there are certainly cases where operators have placed their thumbs on the scales in favor of a preferred option. These choices don’t generally go against what the standards bodies recommend or are working towards. Instead, they satisfy a more immediate internal requirement that doesn’t mesh with the proposed standardization, certification, and product availability timeline defined by the standards bodies and participating equipment suppliers.
Larger operators, including AT&T, BT Openreach, Comcast, and Deutsche Telekom, have also become far more comfortable over the last few years defining standards and pushing them through other industry organizations, such as ONF and the Broadband Forum. These operators know they have the scale and market potential to drive standards and thereby influence the product roadmaps of their incumbent equipment suppliers. There are always others waiting in the wings or the threat of moving to completely virtualized, white box solutions that would reduce the revenue opportunity for said vendors.
And that’s what appears to be happening with 25G PON. Service providers that are part of the MSA are certainly voting with their pocketbooks. Nokia, for its part, has made things quite simple for these operators: Use GPON and XGS-PON today for the bulk of your residential FTTH deployments, and then add in 25G PON using the same equipment and ODN where it makes strategic sense. Nokia does indeed seem to be seeding the market, has reported a cumulative total of 200k 25G-Ready PON OLT ports through 3Q21, with a bigger jump expected in the fourth quarter.
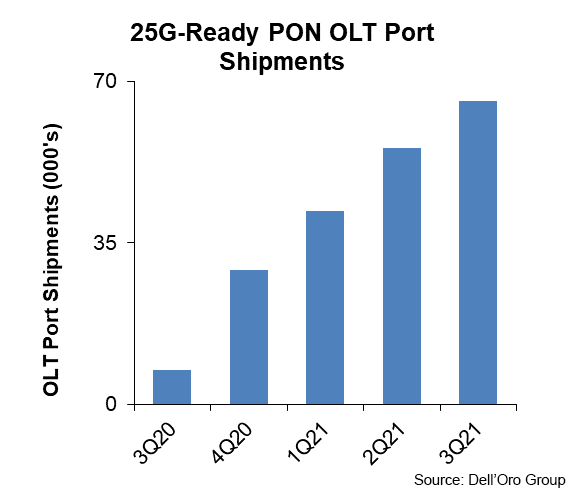
Nokia realizes it must make hay now while the timeline around 50G PON remains in flux and demonstrations of its performance in labs remain limited.
But the PON market has always been one offering different technology options to suit each operator’s unique use case requirements and competitive dynamics. That flexibility is proving to be particularly beneficial in today’s hypercompetitive broadband environment, in which each operator might have a different starting point when it comes to fiber deployments, but likely has similar goals when it comes to subscriber acquisition and revenue generation. In this environment, many operators have clearly said that they simply can’t wait on a promising technology when they need to establish their market presence today. And so, the vendor ecosystem has responded again with options that can steer them down a path to success.