Two weeks ago, the Dell’Oro Group and Huawei jointly hosted a webinar focused on how the integration of Artificial Intelligence and machine learning into home broadband devices can help service providers globally deliver more powerful, customized broadband services to their subscribers. I had the opportunity to provide some market statistics and overall trends in the areas of home networking, while my co-presenters from Huawei and Russia’s Rostelecom, provide more insight into the technical requirements as well as new business opportunities these technologies can deliver.
A major part of recent and ongoing upgrades to home networking devices has been the integration of centralized, cloud-based management, along with machine learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities to more efficiently understand home networking requirements and consumption and optimize services within the home to ensure consistent user experience.
At the same time as machine learning and cloud-based management of CPE are being introduced, Wi-Fi 6 is quickly being integrated into the next generation of home gateways and routers to improve physical layer throughput for the gigabit age. With a focus on providing a theoretical maximum of 10 Gbps of throughput, one of the primary goals of Wi-Fi 6 is to ensure that a customer’s Wi-Fi network will not impede the delivery of high-bandwidth, latency-sensitive services such as cloud gaming, 8k video, and cloud VR services.
This combination of machine learning, AI, and Wi-Fi 6 is giving service providers a toolset they’ve never had before to not only improve how they deliver Wi-Fi services to home broadband subscribers but also how they can tailor and customize their broadband and Wi-Fi offerings to each user, based on their consumption requirements. The net result is a powerful new revolution in-home Wi-Fi.
Using AI to Reduce Latency and Increase Revenue
One of the areas where the combination of machine learning, AI, and Wi-Fi 6 is most effective is in reducing latency throughout home Wi-Fi networks, thereby enabling high-value services such as cloud gaming and cloud VR services.
The reduction in latency allows service providers to tailor their broadband service offerings to specific customer types, especially those who are willing to pay for premium performance for applications such as cloud gaming, which is very sensitive to the impacts of latency.
These same operators are also delivering constant improvements to the performance of their gaming service through the use of machine learning. As bandwidth consumption ebbs and flows throughout the day or during specific hours of the day, the operator can re-route the high priority traffic automatically and dynamically. This can occur both within their own network and also within the home, where less-congested Wi-Fi channels can be quickly identified and used to deliver the latency-sensitive traffic.
Rostelecom has introduced a cloud gaming service in conjunction with gaming platform providers throughout Russia. The service takes advantage of network enhancements Rostelecom has made to offer a premium broadband service tier specifically for online gamers. The service offers near-symmetric speeds and reduced latency to give online gamers an edge over their competitors. Rostelecom expects to take the principle of customized bandwidth tiers to other applications, potentially addressing subscribers who work from home exclusively and need additional throughput and reductions in latency to support HD videoconferencing, for example.
This is but one of the very early examples of AI and machine learning changing the business model of home broadband in positive ways for service providers. We are already seeing operators offer parental controls, device, and user profile controls, as well as new service tiers, tailored specifically to how subscribers actually use bandwidth. Ultimately, just providing a pipe and reliable connectivity won’t be enough for broadband subscribers. Instead, they’ll be asking providers for personalized bandwidth and services. Those services require more intelligence in the home, as well as throughout the access network. Those services will also require end-to-end automation and provisioning so that they can be turned on and off instantly. The integration of AI and machine learning capabilities from the home all the way into the access network will be key enablers of those services going forward.
Click here to watch the on-demand webinar – AI Reshapes Home Networks Experience (pre-registration is required)



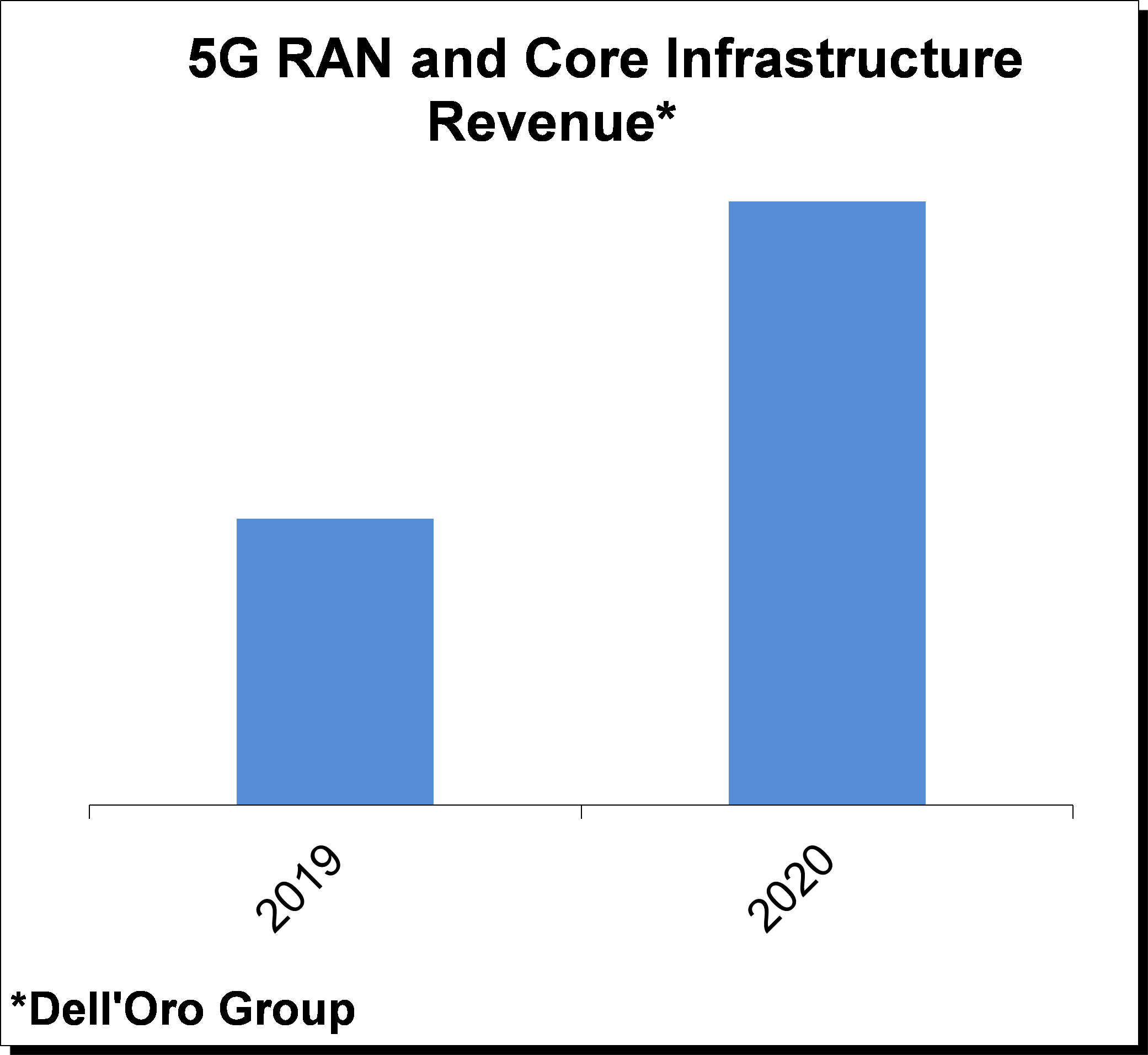 With 5G deployments now accelerating at a torrid pace and 5G NR investments projected to comprise 30% to 50% of global RAN investments in 2020 (Dell’Oro Group), operators are reassessing how to optimize their spectrum resources to capitalize on the potential business and technology benefits with 5G NR. Many countries are realizing the strategic importance of timely 5G deployments spurring governments and regulators to actively release/award 5G spectrum. Even with some minor spectrum auction delays as a result of Covid-19, countries that have auctioned or plans to award sub 6 GHz spectrum by year-end 2020 together comprise nearly 90% of worldwide GDP. At the same time, the amount of spectrum and the type of spectrum that is available varies widely across the globe, prompting operators to effectively capitalize on their respective spectrum assets to build 5G networks with optimal experience.
With 5G deployments now accelerating at a torrid pace and 5G NR investments projected to comprise 30% to 50% of global RAN investments in 2020 (Dell’Oro Group), operators are reassessing how to optimize their spectrum resources to capitalize on the potential business and technology benefits with 5G NR. Many countries are realizing the strategic importance of timely 5G deployments spurring governments and regulators to actively release/award 5G spectrum. Even with some minor spectrum auction delays as a result of Covid-19, countries that have auctioned or plans to award sub 6 GHz spectrum by year-end 2020 together comprise nearly 90% of worldwide GDP. At the same time, the amount of spectrum and the type of spectrum that is available varies widely across the globe, prompting operators to effectively capitalize on their respective spectrum assets to build 5G networks with optimal experience.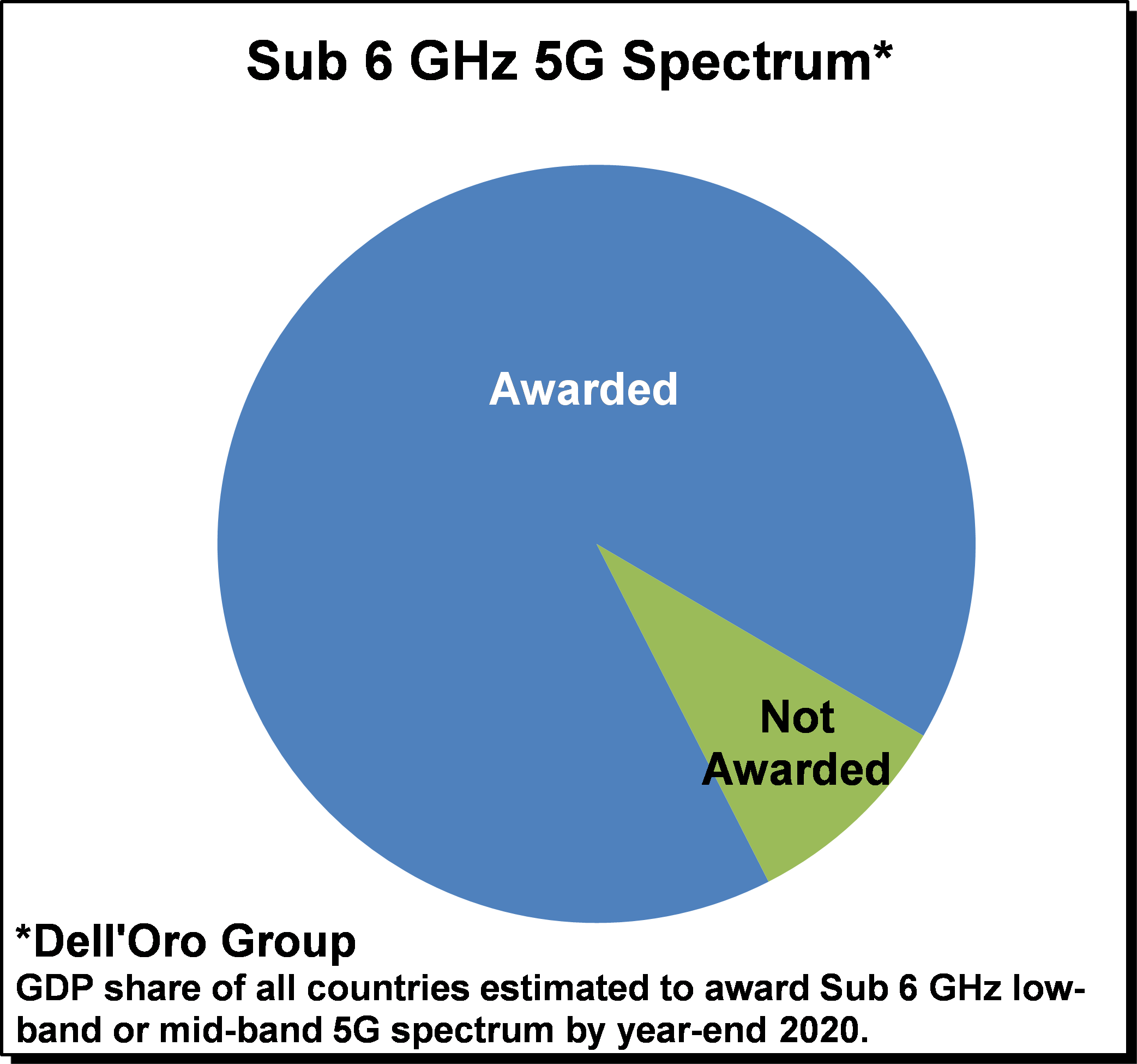 One of the more compelling features with 5G in addition to the increased spectrum bandwidth that comes with the upper mid-band and the mmW spectrum is the fact that 5G NR offers spectral efficiency improvements on a like for like basis relative to LTE, implying that operators and eventually enterprises can take advantage of these efficiency benefits regardless of their current spectrum portfolio. And in contrast to previous mobile technology transitions, new technologies such as dynamic spectrum sharing, dual connectivity and carrier aggregation across multiple technologies will provide the necessary tools to simplify and accelerate the migration from LTE to 5G NR. This improved flexibility taken together with the efficiency and performance upside with 5G NR plays an important role in the improved market sentiment that has characterized the RAN market in this initial 5G mobile broadband (MBB) deployment phase. While having the right mix of spectrum remains extremely important, the relatively seamless transition enables operators to put parts of the spectrum to use today. It does not matter if the spectrum is optimized for coverage or better suited for capacity or if an operator has a non-ideal portfolio mix of low-band, mid-band, or high-band spectrum. With 5G, operators now have the tools to capitalize on the benefits with the respective bands and put together a roadmap that migrates the portfolio in various phases from legacy 2G-4G to 5G NR.
One of the more compelling features with 5G in addition to the increased spectrum bandwidth that comes with the upper mid-band and the mmW spectrum is the fact that 5G NR offers spectral efficiency improvements on a like for like basis relative to LTE, implying that operators and eventually enterprises can take advantage of these efficiency benefits regardless of their current spectrum portfolio. And in contrast to previous mobile technology transitions, new technologies such as dynamic spectrum sharing, dual connectivity and carrier aggregation across multiple technologies will provide the necessary tools to simplify and accelerate the migration from LTE to 5G NR. This improved flexibility taken together with the efficiency and performance upside with 5G NR plays an important role in the improved market sentiment that has characterized the RAN market in this initial 5G mobile broadband (MBB) deployment phase. While having the right mix of spectrum remains extremely important, the relatively seamless transition enables operators to put parts of the spectrum to use today. It does not matter if the spectrum is optimized for coverage or better suited for capacity or if an operator has a non-ideal portfolio mix of low-band, mid-band, or high-band spectrum. With 5G, operators now have the tools to capitalize on the benefits with the respective bands and put together a roadmap that migrates the portfolio in various phases from legacy 2G-4G to 5G NR.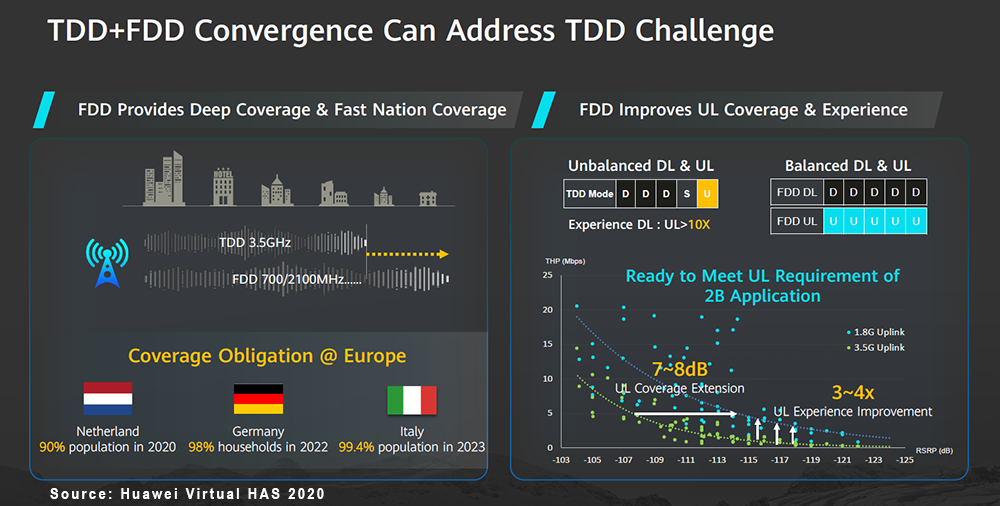
 Given that there is a strong correlation between network services requirements and mobile broadband investments for the more simplified site deployments, this on-going shift towards multi technology sites including both legacy technologies and more complicated 5G solutions that could involve dynamic spectrum sharing and beamforming addressing a wider scope of use cases spanning across potentially multiple industries in combination with the increased site complexity and the need to focus on energy optimization will accelerate the shift towards more intelligent planning/design, operations and predictive analysis.
Given that there is a strong correlation between network services requirements and mobile broadband investments for the more simplified site deployments, this on-going shift towards multi technology sites including both legacy technologies and more complicated 5G solutions that could involve dynamic spectrum sharing and beamforming addressing a wider scope of use cases spanning across potentially multiple industries in combination with the increased site complexity and the need to focus on energy optimization will accelerate the shift towards more intelligent planning/design, operations and predictive analysis.